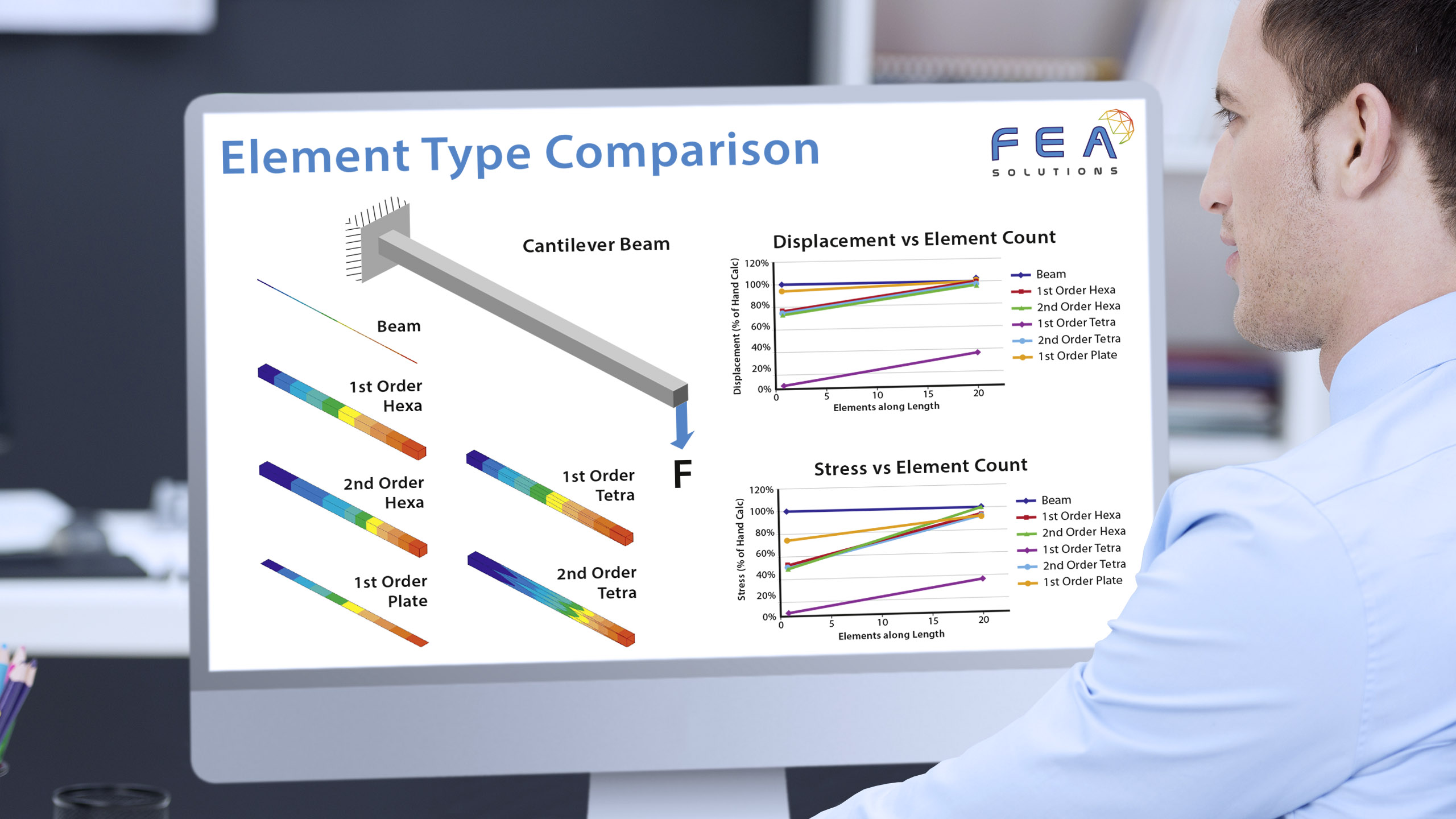
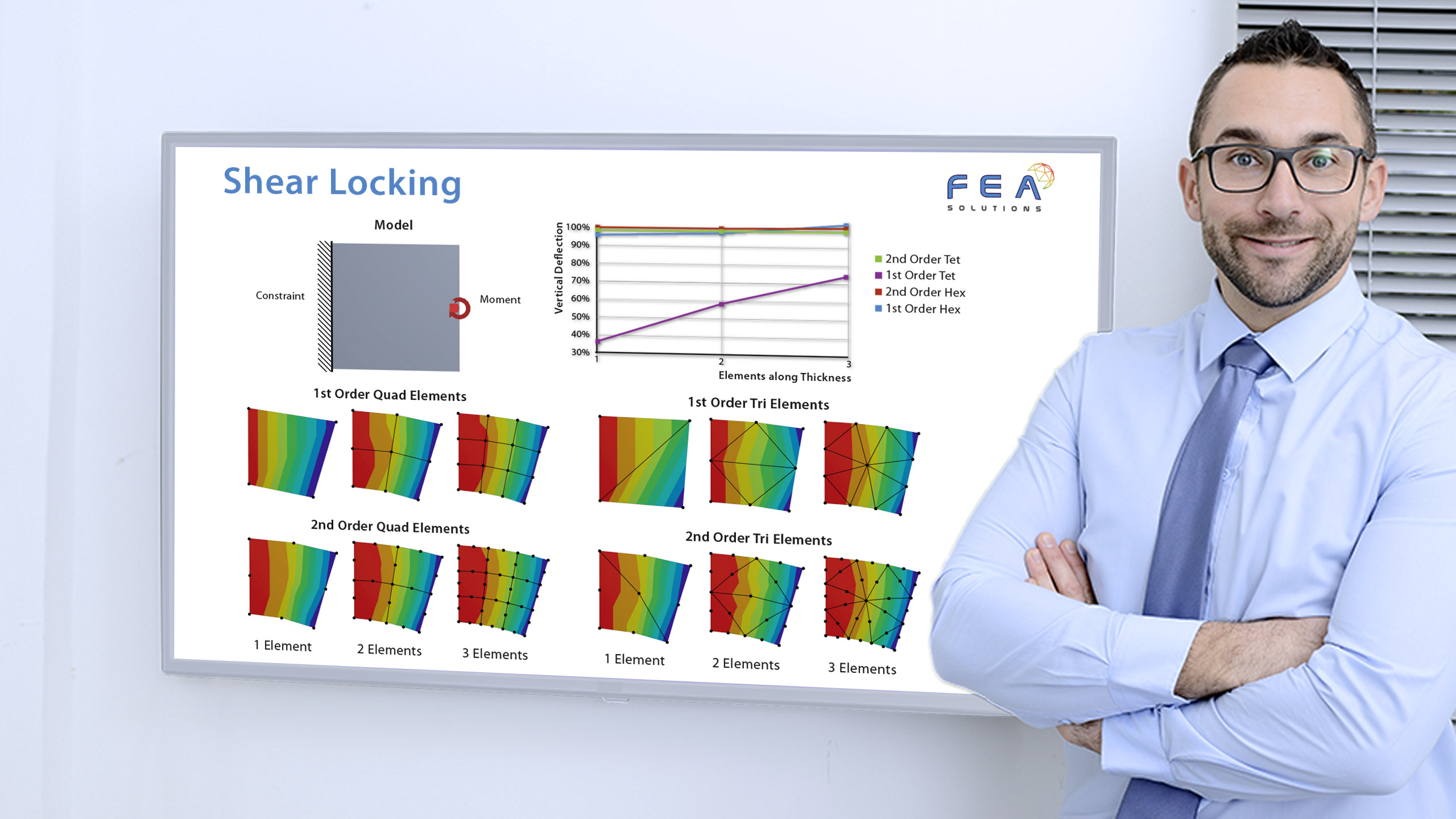
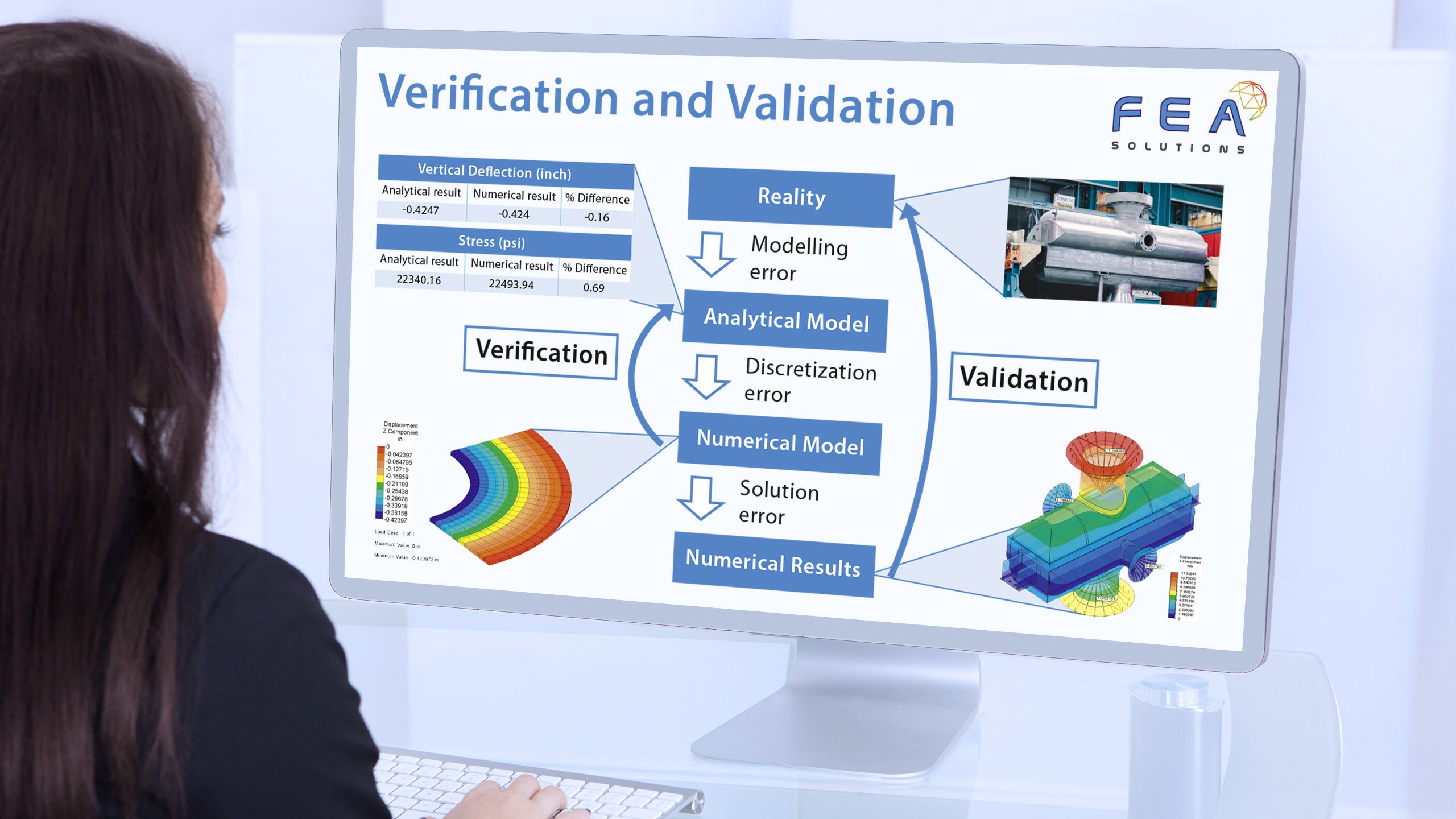
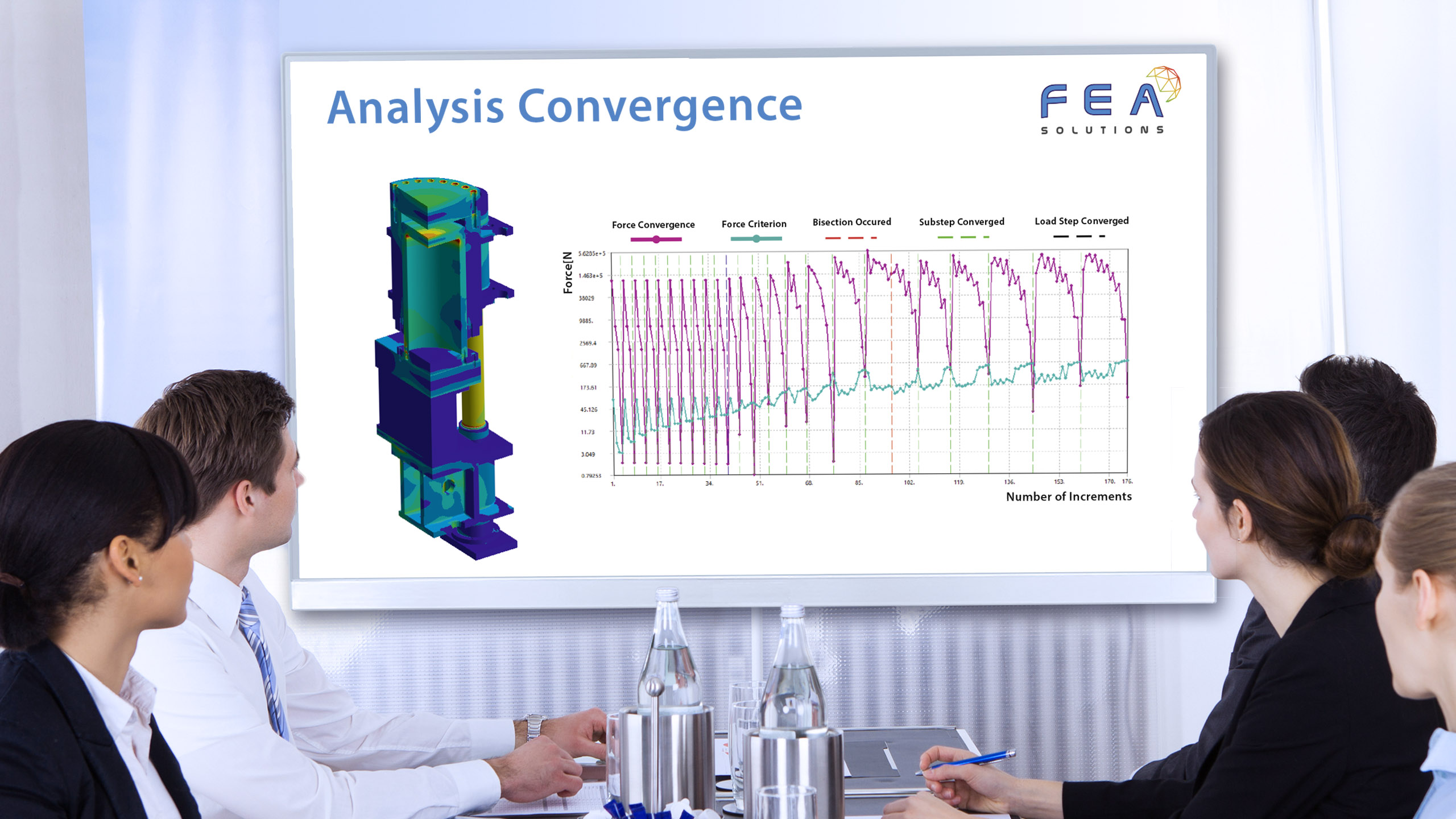
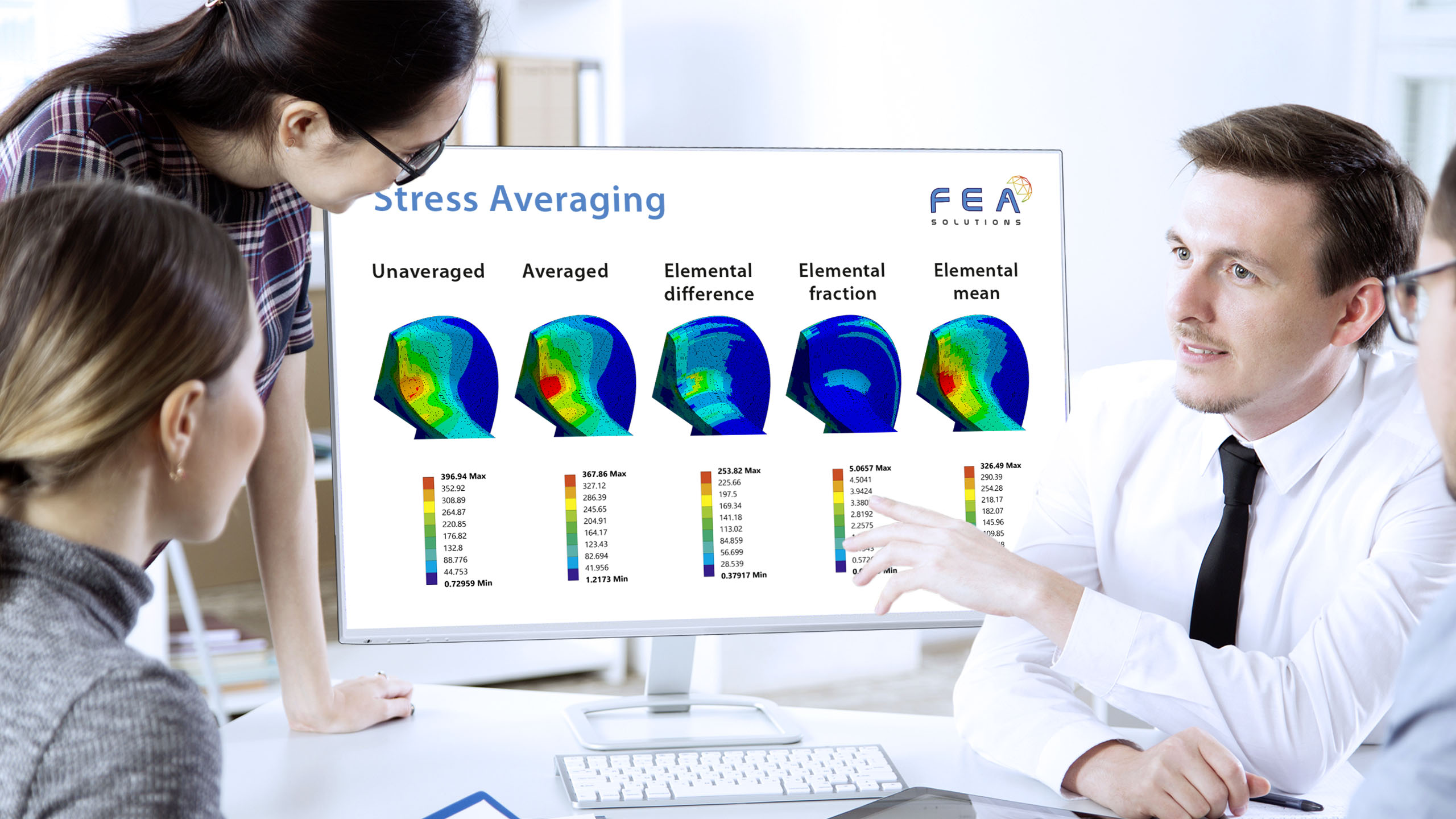
29 Jun Element Type Comparison
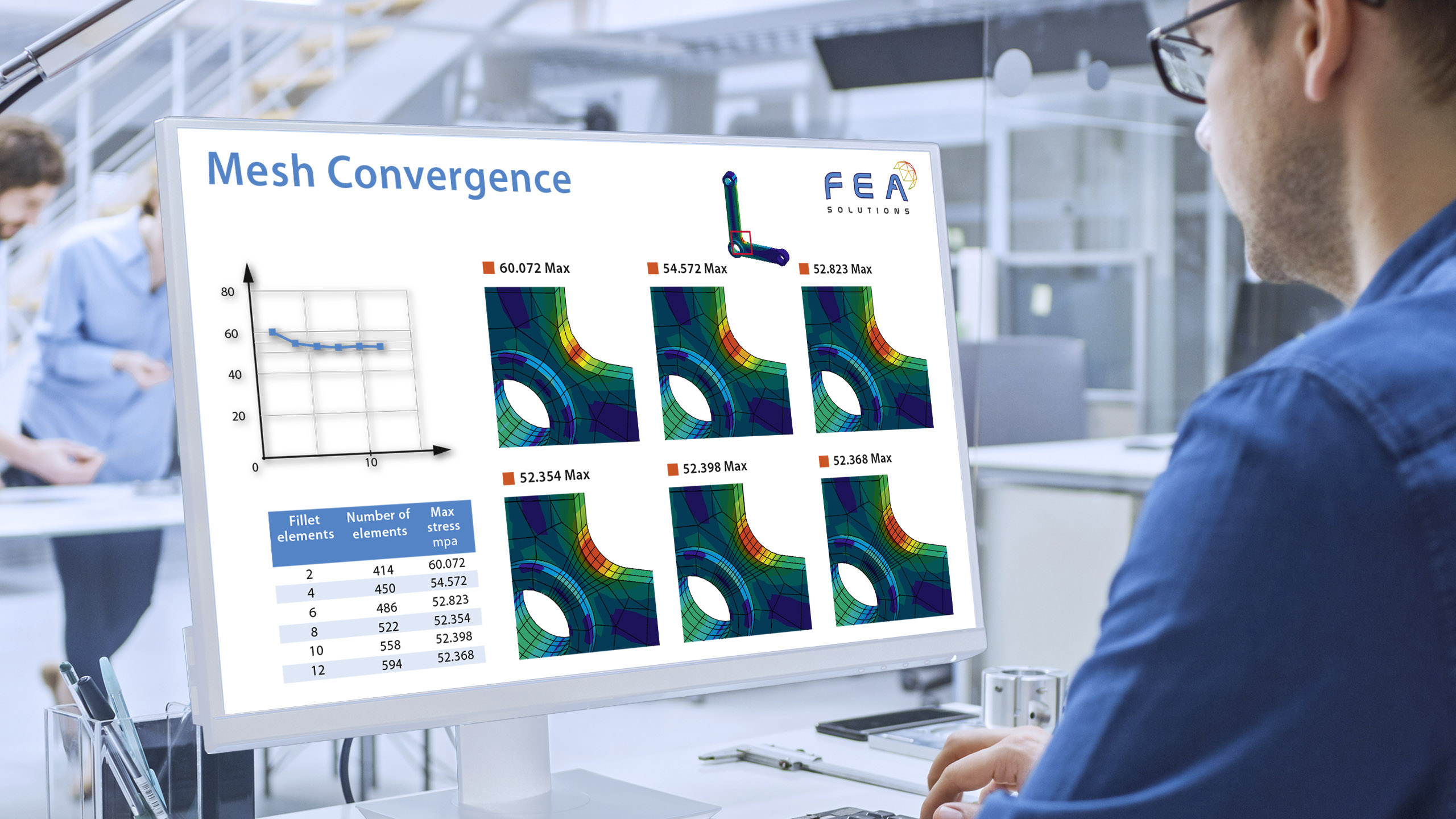
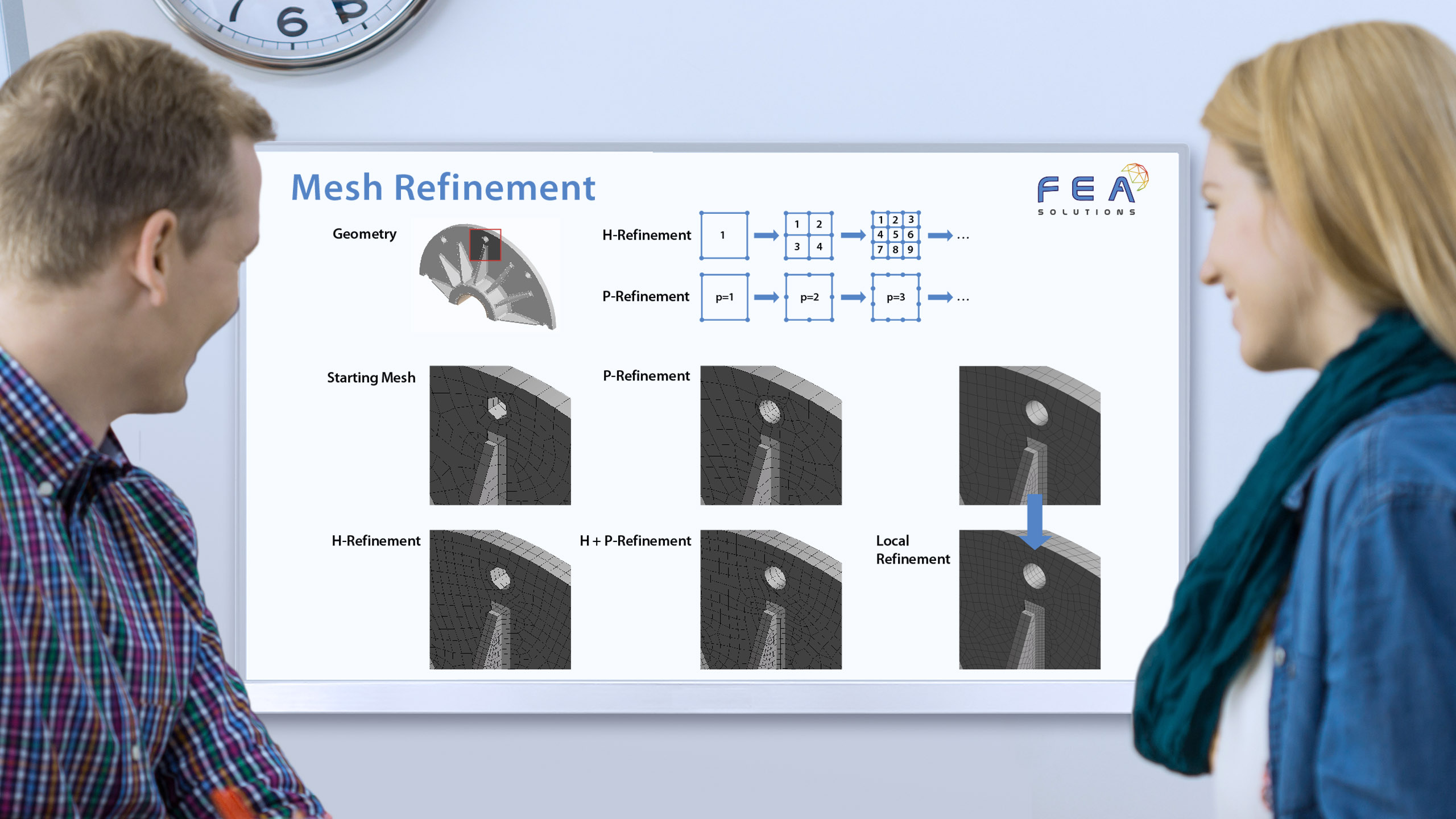
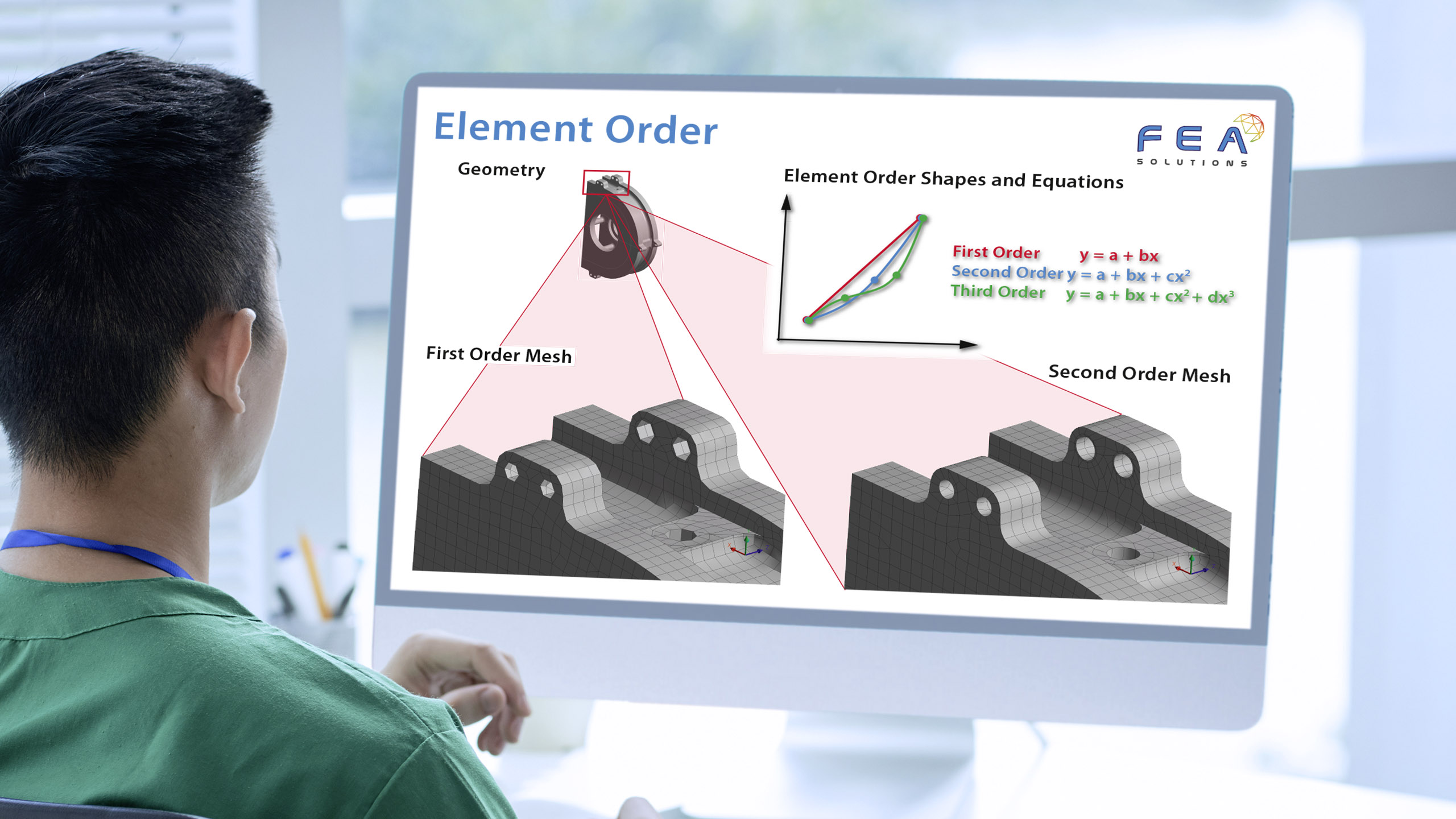
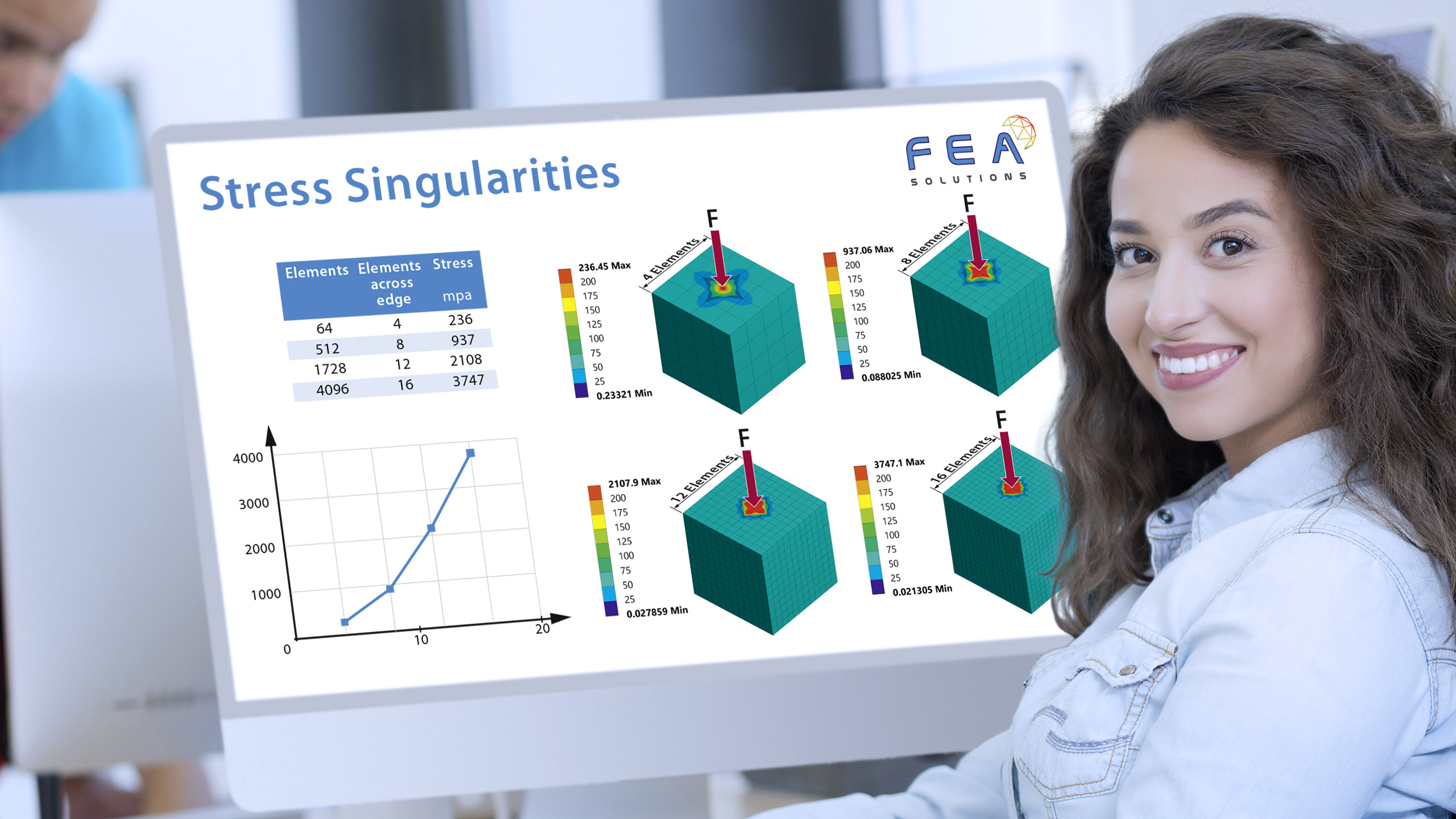
When building a mesh for FEA, there are different types of elements that can be used: - Line elements (https://fea-solutions.co.uk/line-elements/). - Surface elements (https://fea-solutions.co.uk/surface-elements/), e.g. plate or shell elements. - Solid elements (https://fea-solutions.co.uk/solid-elements/), also called volume elements or 3D elements. Because the mathematical model used for line elements consider...