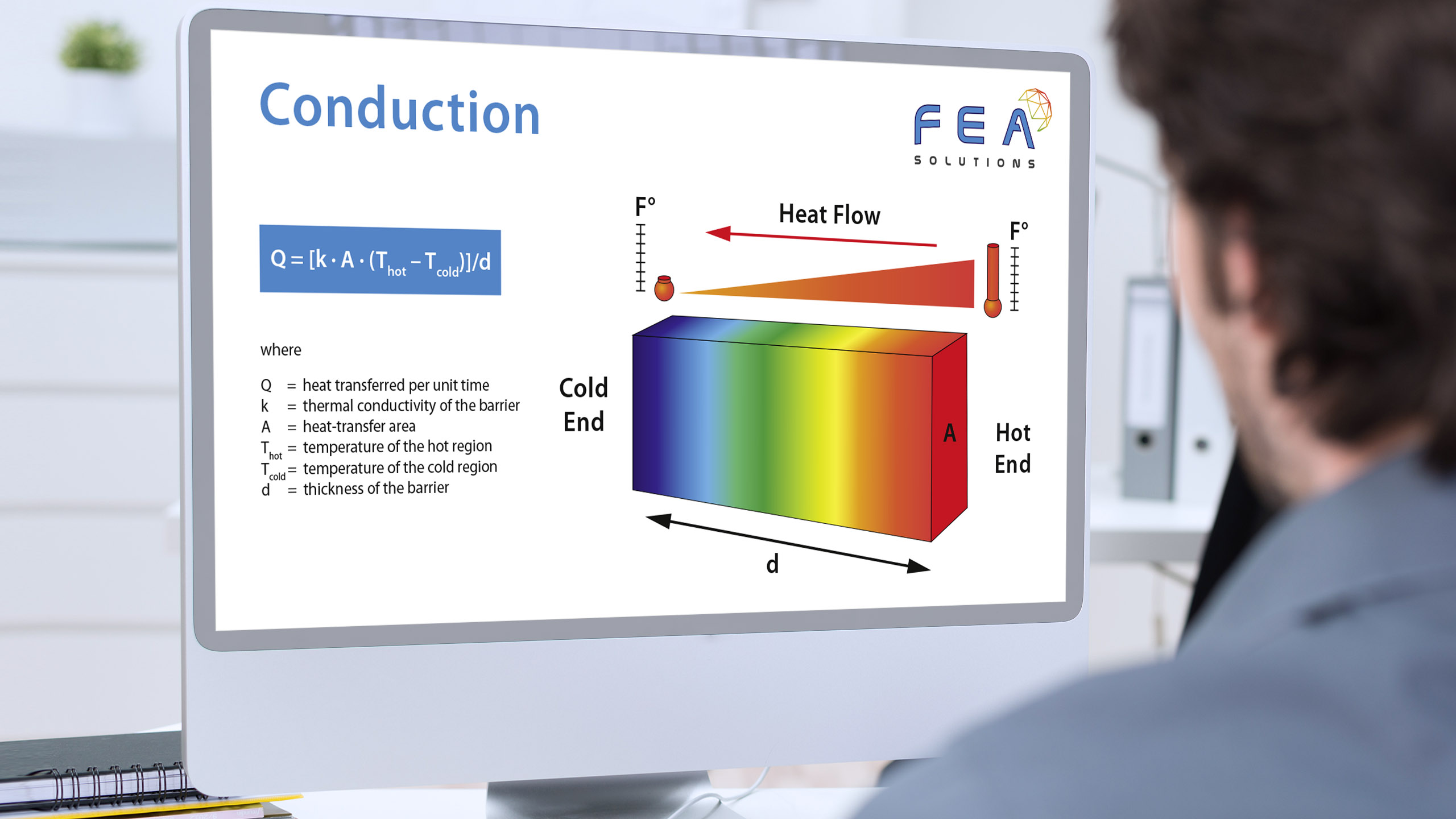
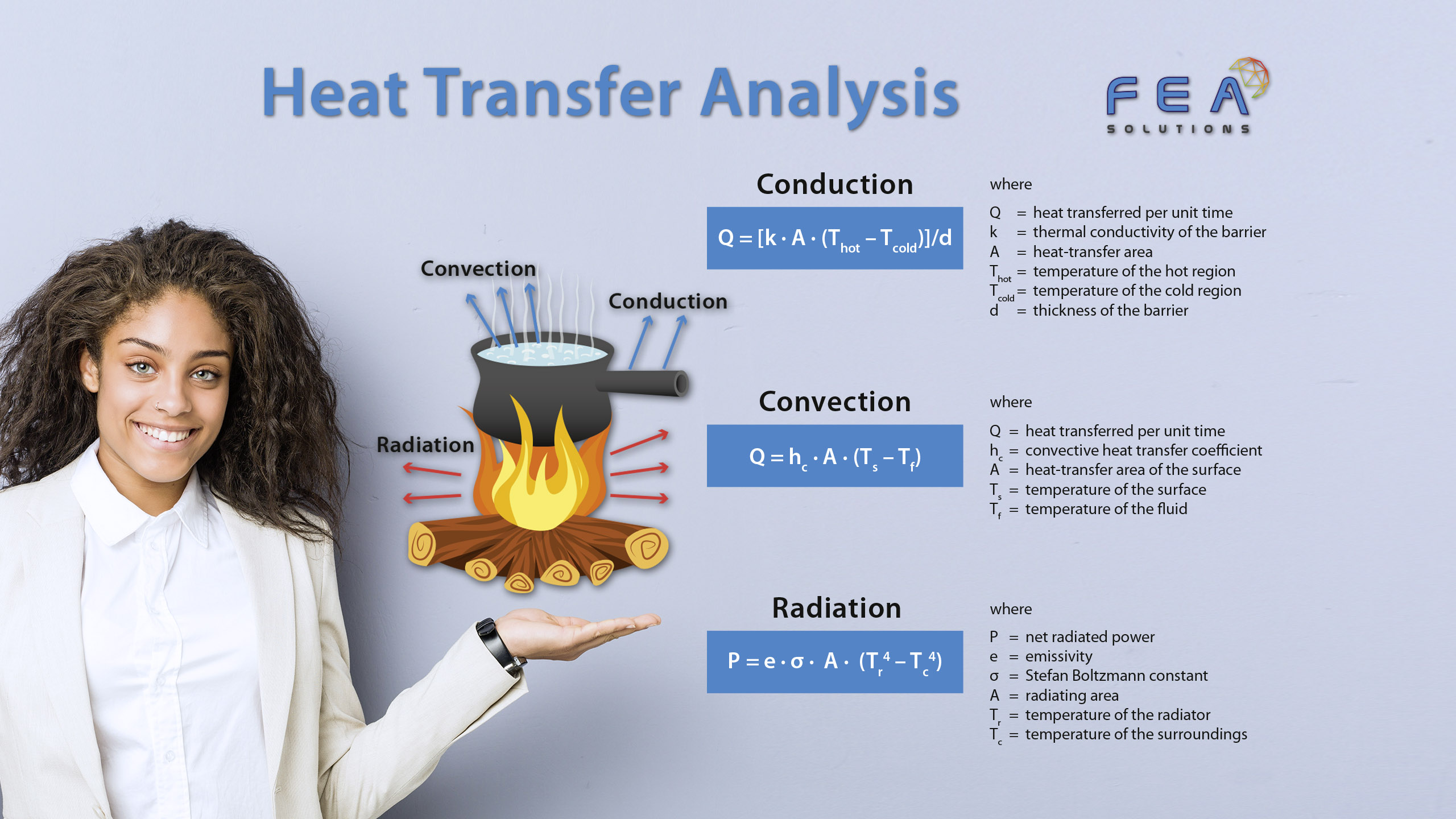
21 Apr Nodal Stress Calculation
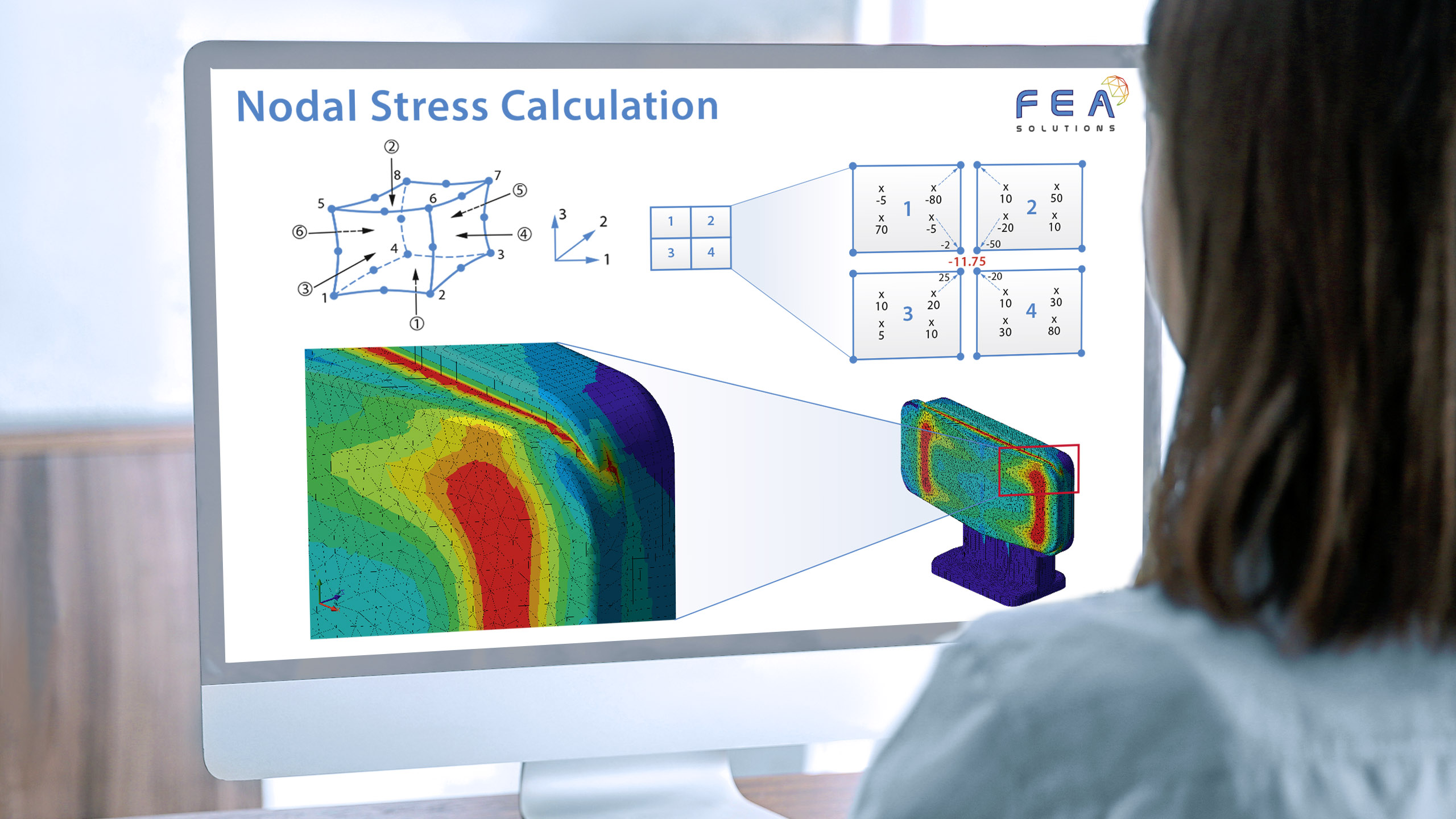
During the static stress analysis of a structure, FEA solves its stiffness matrix. The results of this solution are nodal displacements. That means a FEA stress analysis is actually a displacement analysis. The nodal displacement results are precise, that means each node within the mesh...