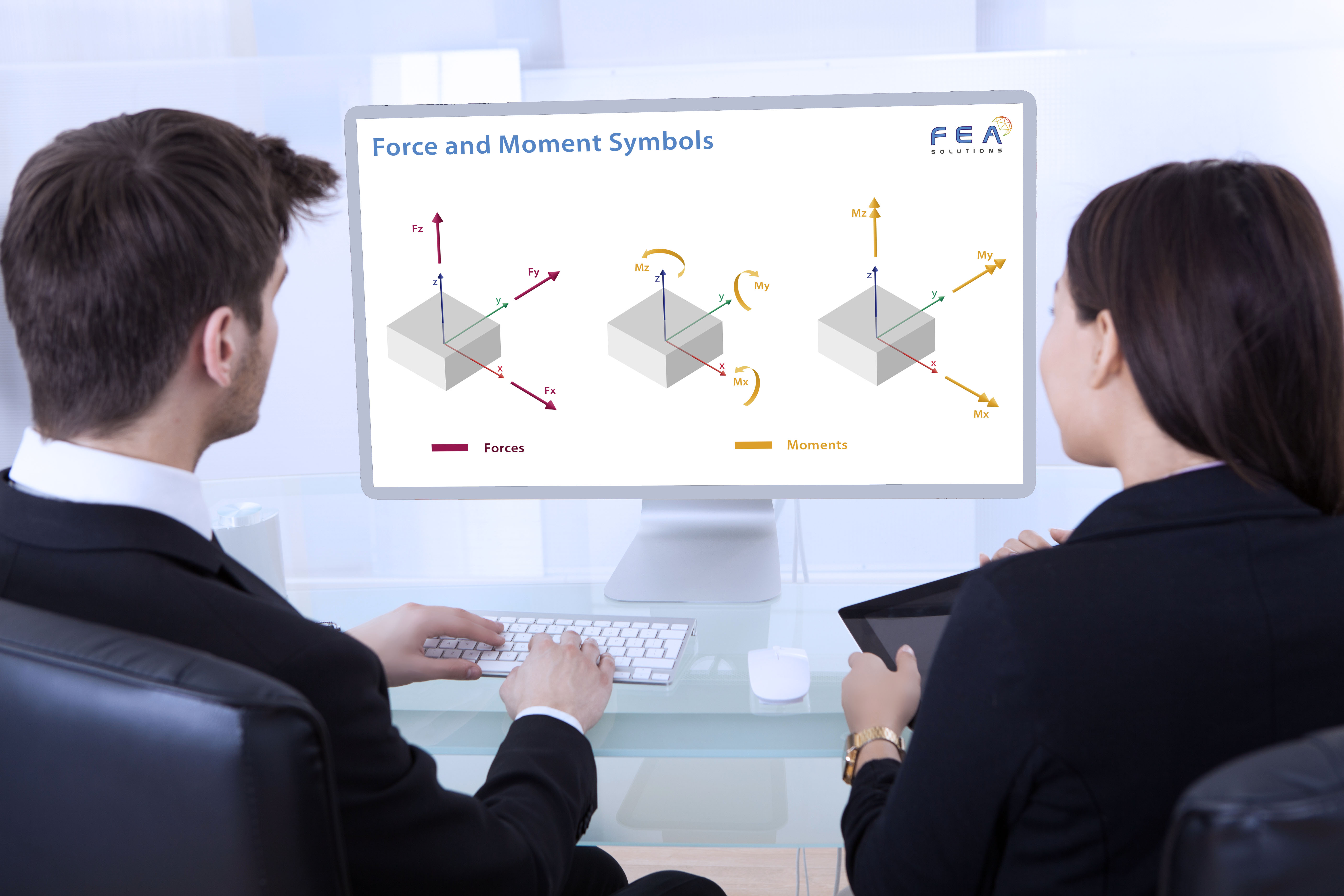
08 Feb Force and Moment Symbols
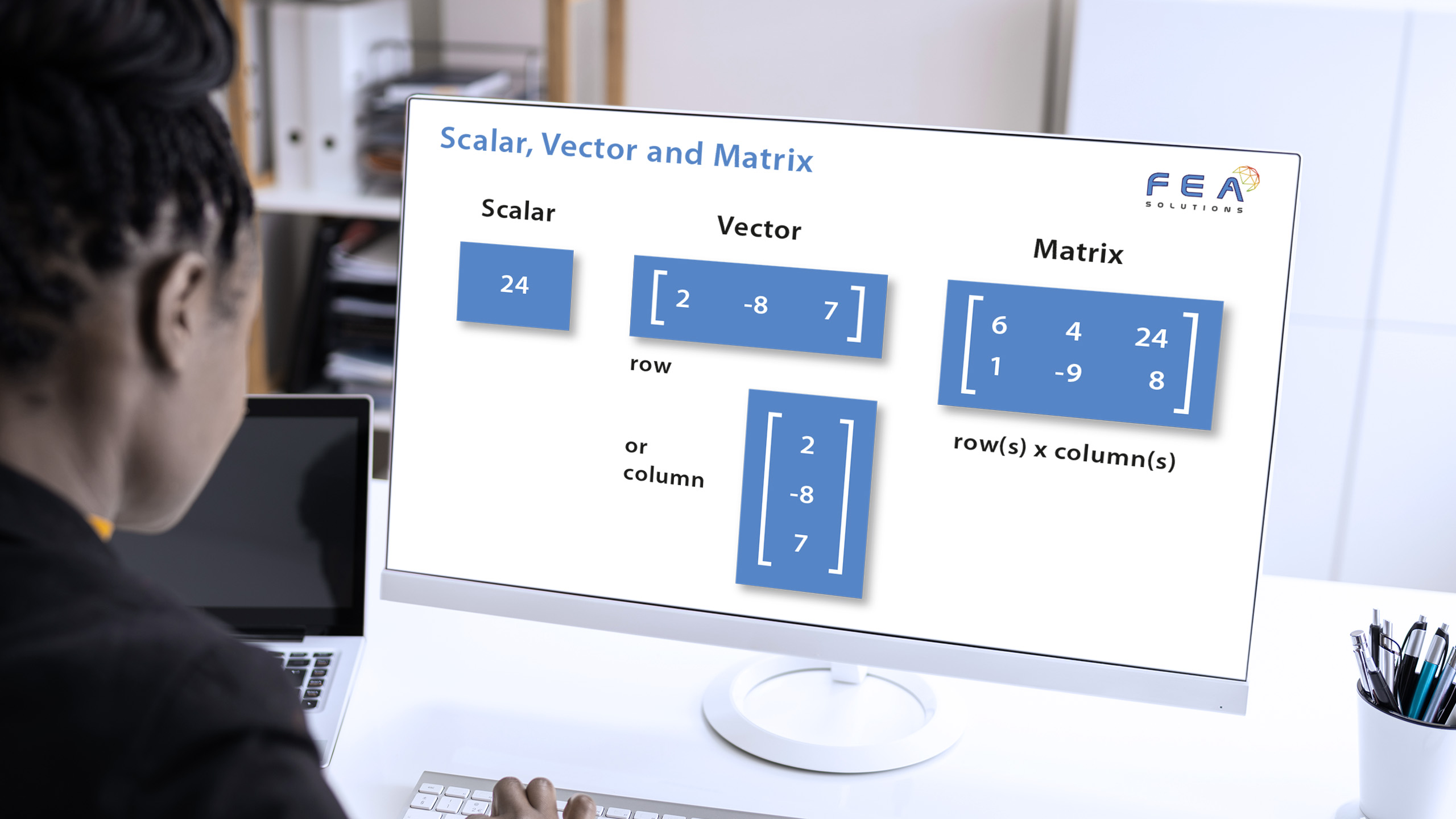
[vc_row css_animation="" row_type="row" use_row_as_full_screen_section="no" type="full_width" angled_section="no" text_align="left" background_image_as_pattern="without_pattern"][vc_column][vc_column_text]In structural mechanics, forces and moments are graphically represented by arrows. For a force, which is vector (https://fea-solutions.co.uk/scalar-vector-and-matrix/), a straight single arrow is used to depict it, pointing in the direction the force is acting. For moments, there are two...